The Power of Open-Source: How Tabiya’s Approach Supports Innovation and Social Impact

Open-source software is a powerful tool for innovation and collaboration, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Unlike proprietary software, which often relies on strong patents and copyrights, open-source solutions are readily available to anyone who wants to study, change, modify or distribute them. That said, it’s important to remember that open source doesn't always have to be separate from proprietary systems; it can be integrated with them or used across different operating systems. Tabiya’s commitment to open-source software, models and standards reflects its mission to tackle the global youth employment challenge, especially in low- and middle-income countries, with a particular focus on informal sectors like care work.
Open Source: An Important Strategy for Economic Accessibility
In low- and middle-income countries, the high cost of proprietary software can be a significant barrier to accessing digital tools. Open-source software alleviates this financial obstacle, making technology available to everyone, regardless of their resources. By offering its tools as digital public goods, Tabiya keeps its solutions accessible to communities globally. For example, Tabiya’s AI-powered Compass tool is open source, allowing developers around the world to contribute and adapt it to local needs (technical overview available here). This open-source model means that Tabiya’s innovations are affordable, scalable and adaptable to diverse contexts.
Open-source software is both cost-effective and highly collaborative. By making its code accessible to anyone, it invites input from global communities, enabling developers worldwide to share knowledge, contribute improvements and drive continuous innovation. This openness encourages more equal partnerships and enhances interoperability through shared standards and collective problem-solving. Moreover, the adaptability of open-source tools allows them to evolve as needs change, keeping solutions effective for both users and developers.
Addressing the Youth Unemployment Crisis in Sub-Saharan Africa
Youth unemployment remains a critical issue, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, where only three jobs are created for every 11 young people entering the workforce. It is estimated that, between 2023 and 2050, the cumulative growth in the youth labor force in sub-Saharan Africa will be 72.6 million, further intensifying this employment challenge. Tabiya addresses this by recognizing and validating skills from the informal economy, creating pathways for young people to enter the formal labor market.
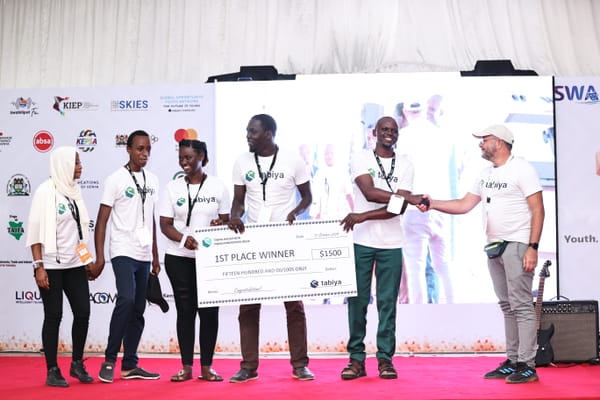
Tabiya’s tools are central to this effort. For example, the Compass conversational tool, the Livelihoods Classifier, and the Taxonomy model were key components of projects during Tabiya’s 2024 hackathon, held in partnership with Swahilipot Hub Foundation at Pwani Innovation Week. This event brought together young developers to design job matching and skills recognition solutions, demonstrating the potential of open-source technology to drive innovation and empower youth employment within local communities.

As an open-source organization, Tabiya strives to make its tools and code base accessible for adaptation to specific needs and contexts. The hackathon raised awareness of our products and tested their accessibility for integration by others. We’ve learned the importance of developing an API for easier integration, which will inform our use case this year. Tabiya is planning another hackathon in Kigali, Rwanda, this spring.
Localized and Adaptable Solutions
One of the key strengths of Tabiya’s open-source model is its ability to be adapted for different regions. Central to this is our Inclusive Livelihoods Taxonomy. Building on the European Skills, Competences, Qualifications and Occupations (ESCO) taxonomy, the Inclusive Livelihoods Taxonomy categorizes a wide range of skills and occupations, including informal work and non-traditional pathways, providing a valuable framework for job matching. It can be localized to meet the specific needs of different regions. For example, our first localization is in South Africa, where we are partnering with Harambee Youth Employment Accelerator to tailor the taxonomy for the local context.
One challenge to localization is language. While most developers understand English, not all can fully grasp the technical documentation and specifications needed to contribute to an open-source project. To address this, our multicultural team is working towards translating documentation to French, with plans to expand to more languages in the future. Additionally, we prioritize cultural sensitivity in academic research, meaning our open-source models are adaptable across diverse contexts.

Infrastructure and Technical Barriers to Open-Source Adoption
While open source offers many benefits, its adoption is not without challenges. In many low- and middle-income countries, technical barriers such as poor internet access, weak infrastructure and limited digital literacy hinder the widespread use of open-source software. In addition, political and cultural factors, such as insufficient intellectual property protection, can slow down the adoption of open-source solutions.
Nevertheless, Tabiya is actively working to overcome these barriers. By developing tools that are lightweight and designed to work in low-bandwidth environments, Tabiya’s solutions can be used in regions with limited internet access. Moreover, Tabiya’s collaboration with local organizations, such as through hackathons, encourages a culture of innovation and helps build local expertise in the use and development of open-source software.
The Importance of Keeping Tabiya’s Work Open Source
Keeping Tabiya’s solutions open source is essential for achieving strong social impact. Open source allows for the continuous input of global contributors and adoption by users, so that the tools remain dynamic and adaptable to ever-changing needs. What’s more it ensures that these tools remain affordable and accessible to all, particularly those in low- and middle-income countries who may not have the resources to implement proprietary software.
Incorporating community-driven innovation is at the heart of Tabiya’s approach. By engaging developers and users in the creation and improvement of tools, Tabiya ensures that its solutions are always evolving to meet the needs of local communities. This model not only accelerates innovation but also builds a sustainable ecosystem around Tabiya’s tools, enabling them to grow and thrive over time.
Achieving Tangible Outcomes Through Open Source
Tabiya’s adoption of open-source principles has already led to tangible outcomes. For example, Compass is helping organizations worldwide adapt to local labor market conditions by recognizing informal sector skills and facilitating job matching. Moreover, by opening up its innovations to global collaboration, Tabiya is creating opportunities for developers and organizations to contribute to the growth of its tools, expanding their reach and impact.
Tabiya hopes to continue to improve and evolve its suite of open data, models and standards through collaboration with partners, researchers and advocates. By collaborating with communities committed to open innovation, we aim to refine our tools, expand their reach and ensure they remain accessible and adaptable to the evolving needs of job seekers. We hope to achieve sustainable changes in low- and middle-income country labor markets, driving broader economic participation and supporting long-term development.